You have no items in your shopping cart.
Description
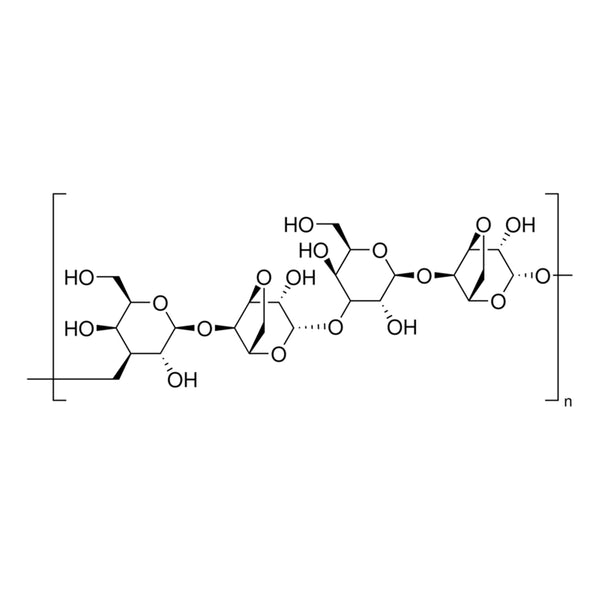
Agarose is a polymer extracted from agar or agar-bearing marine algae. This purified linear galactan hydrocolloid comprises alternating co-polymers D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose units connected by α-(1→3) and β-(1→4) glycosidic bonds. Agarose is highly biocompatible and possesses variable mechanical and diffusion properties. Agarose can be used as a gelling agent, to separate nucleic acids electrophoretically.
Specification
| Grade | Biotech |
| CAS | 9012-36-6 |
| Appearance | Fine, homogeneous powder |
| Color | White |
| Particle Size(A.S.T.M.) | Report |
| Moisture | ≤10% |
| Ash | ≤2.0% |
| Electroendosmosis-Mr (pH 8.4, Wieme method) | ≤0.12 |
| Sulfate (%) | ≤0.15% |
| Gel Test (1.5%) | |
| pH in solution | 6.0-7.5 |
| pH in gel | 7.0±0.5 |
| Colorimetry (Absorbance) n m u 450 | Report |
| Gel Strength | ≥480 g/cm2 |
| Gelling temperature | 26±0.5℃ |
| Melting temperature | 62-68℃ |
| Storage | RT, protect from moisture. |
Application
Agarose has been used:
-
in thaumatin and elastase protein crystallization
-
in microcasting using a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) mold with micro-channel
-
in agarose micro-confinement array
Agarose is super low melting point and recommended for use in capillary electrophoresis, tissues & cell culture, and viral plaque assay.
Yields unusually strong gels for an ultra-low gelling agarose. Ideal for electrophoresis of heat-labile samples and for growth of hybridomas or other cell lines.
Analysis Note
The following is a list of properties associated with our agaroses:
Sulfate content - used as an indicator of purity, since sulfate is the major ionic group present.
Gel strength - the force that must be applied to a gel to cause it to fracture.
Gel point - the temperature at which an aqueous agarose solution forms a gel as it cools. Agarose solutions exhibit hysteresis in the liquid-to-gel transition - that is, their gel point is not the same as their melting temperature.
Electroendosmosis (EEO) - a movement of liquid through the gel. Anionic groups in an agarose gel are affixed to the matrix and cannot move, but dissociable counter cations can migrate toward the cathode in the matrix, giving rise to EEO. Since electrophoretic movement of biopolymers is usually toward the anode, EEO can disrupt separations because of internal convection.
Documents
Disclaimer: For laboratory research use only.
When can I expect my order to ship?
Most orders are filled and shipped within 2-3 business days from the time they are received.
Our standard shipping usually take 2-5 days.
We also provide express shippping for time-sensitive deliveries.
Email contact@biofargo.com if you have any requirements.